Portfolio Management
Many advisors employ cookie-cutter, algorithm driven portfolios. Not us. We invest time to know our clients. Our recommendations will be geared towards your specific goals, timeframe, and risk tolerance. We will never ask you to accept our recommendations in blind faith. Dublin Capital Management is committed to educating clients. Our first test for success is the Sleep Test – does your plan give you confidence to sleep well at night?
We offer investments as Registered Representatives of LPL Financial, the nation’s leading broker-dealer* for independent financial advisors. Being independent allows us to always put the clients’ interests first in the advice we give and the products we recommend.
*As reported by Financial Planning magazine, June 1996-2019, based on total revenue.
Current Portfolio - All Assets
- Bonds
- US – Large Cap
- US – Mid Cap
- US – Small Cap
- Developed International
- Emerging Markets
- Other Income
- Cash
Target Portfolio
- Bonds
- US – Large Cap
- US – Mid Cap
- US – Small Cap
- Developed International
- Emerging Markets
- Other Income
- Cash
*Sample Portfolio Data Profiles
Investing
The Blended Rate is the weighted average of the market index rates of returns that underlie each asset class of a given model portfolio. Account fees are not taken into consideration.
All investments involve risks that you will lose value including the amount of your initial investment. Investments that offer the potential for higher rates of return generally involve greater risk of loss.
- International investing: There are special risks associated with international investing, such as political changes and currency fluctuations. These risks are heightened in emerging markets.
- Small/Mid-Capitalization investing: Investments in companies with small or mid-market capitalization (“small/mid-caps”) may be subject to special risks given their characteristic narrow markets, limited financial resources, and less liquid stocks, all of which may cause price volatility.
- High-Yield investing: Investments in high yielding debt securities are generally subject to greater market fluctuations and risk of loss of income and principal, than are investments in lower yielding debt securities.
- Inflation Protected Bond investing: Interest rate increases can cause the price of a debt security to decrease. Increases in real interest rates can cause the price of inflation- protected debt securities to decrease. Interest payments on inflation-protected debt securities can be unpredictable.
- Interest Rate Risk: This risk refers to the risk that bond prices decline as interest rates rise. Interest rates and bond prices tend to move in opposite directions. Long-term bonds tend to be more sensitive to interest rate changes and therefore may be more volatile.
Note: reinvestment transactions that involve selling existing investments may involve transaction costs associated with the sale of those assets as well as transaction costs associated with the purchase of new investments.
Discover Your Risk Tolerance Level.
20% Stocks / 80% Bonds
A Conservative Risk Tolerance offers the least amount of risk.
40% Stocks / 60% Bonds
A Moderate Conservative Risk Tolerance Level falls in between a conservative level of risk and a moderate level.
60% Stocks / 40% Bonds
A Moderate Risk Tolerance Level falls directly in the middle of Conservative and Aggressive Risk ranges.
80% Stocks / 20% Bonds
A Moderate Aggressive Risk Tolerance Level falls in between a moderate level of risk and an aggressive level.
100% Stocks / 0% Bonds
The Aggressive range of Risk Tolerance involves the most risk.
Risk Vs. Return
One important aspect of assessing an investment portfolio is to consider its allocation amongst the various classes of assets (cash, bonds and stocks) within the portfolio. Financial advisors generally recommend investors diversify their investment holdings across these asset classes in various combinations to spread investment risk. Investment risk can be measured by Standard Deviation, a statistical measure of the variability of a set of data.
Diversification is achieved through investment in a combination of asset classes that historically have performed differently. Investments that historically have performed opposite from one another are said to be negatively correlated. The goal is to construct a portfolio allocation with a risk-return profile that aligns with the investor’s risk tolerance level and investment objectives and lies on the Efficient Frontier.
The Efficient Frontier is the theoretical combination of minimum investment risk for a given target investment return. Other portfolios that have the same level of risk would have a lower return potential and would therefore be inefficient.
Efficient Frontier
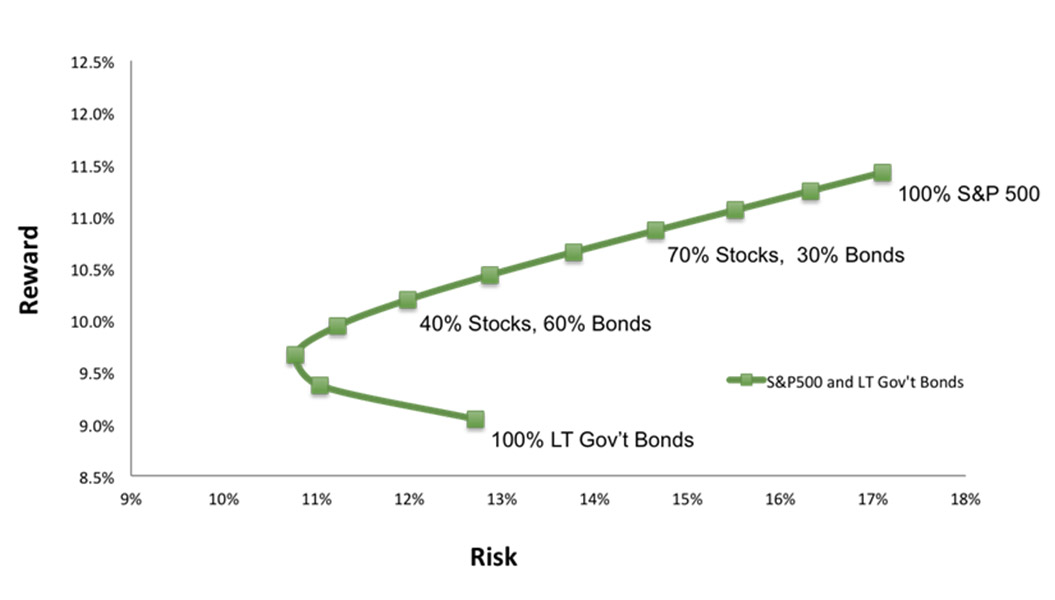
Combining Two Asset Classes 1978-2010
Results shown are based on indexes and are illustrative; they assume reinvestment of income and no transaction costs or taxes. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. Direct investment cannot be made in an index. Results are not meant to represent a recommendation but rather are an example of how adding asset classes can adjust the Efficient Frontier. Data source DFA.
There is no guarantee that a diversified portfolio will enhance overall returns or outperform a non-diversified portfolio. Diversification does not ensure against market risk.












